FAQ
Applications of Printed Radioactive Materials
What Types of Applications of Printed Radioactive Materials Have Been Demonstrated?
Phantoms
3D printing of radioactive phantoms has been successfully demonstrated and represents a promising application for quality control of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) systems.

|
|

|
Seeds
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation source (the seed) is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. Seeds for brachytherapy can be 3D printed using radioactive materials.
What Are Phantoms for PET/SPECT?
In medical imaging, particularly in Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), a "phantom" is a specially designed object that mimics the properties of human tissues and organs. Phantoms are used for a variety of purposes, including the calibration, testing, and quality assurance of imaging systems.
What Are Seeds for Brachytherapy?
In brachytherapy, "seeds" refer to small, radioactive sources that are implanted directly into or near a tumor to deliver localized radiation treatment. This method is commonly used for treating various types of cancer, including prostate, cervical, and breast cancer. The seeds provide a high dose of radiation to the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
What Types of Radionuclides Have Been Discussed for Printing Phantoms for PET/SPECT?
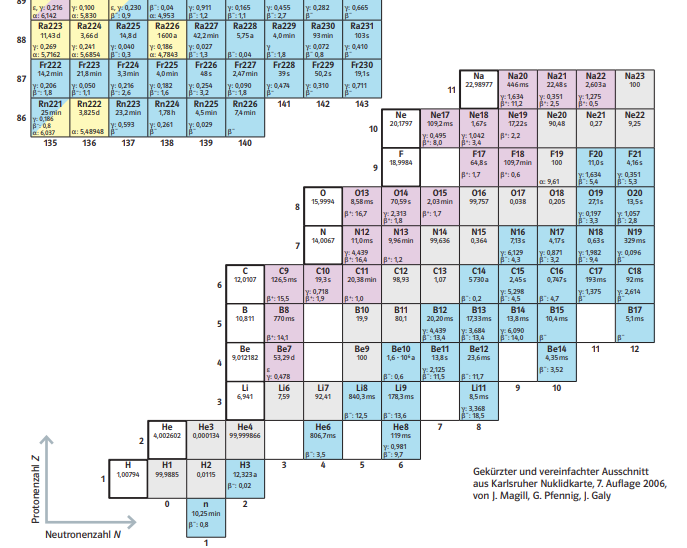
The following radionuclides have been considered for printing phantoms: Na-22, Ga-68, Ge-68, Co-57, Tc-99, Lu-177, F-18, and others.
What Types of Radioactivity Exist?
Alpha Radiation
During alpha decay, the decaying atomic nucleus emits a helium-4 atomic nucleus (alpha particle), which consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Alpha radiation has low penetration and can be shielded by a thin sheet of paper.
Beta Radiation
Beta radiation is divided into two types: beta-minus and beta-plus radiation:
- In beta-minus decay, a neutron in the atomic nucleus is converted into a proton, producing an electron that is emitted.
- In beta-plus decay, a proton in the atomic nucleus is converted into a neutron, producing a positron that is emitted.
Beta radiation can typically be shielded by materials just a few millimeters thick, such as PMMA, glass, or a thin metal plate.
Gamma Radiation
An excited nucleus with increased energy emits wave-like gamma radiation as it "oscillates" rapidly. Gamma radiation, a type of electromagnetic radiation, easily penetrates matter and requires a thick layer of concrete or lead for shielding.
What About Regulations of Radioactivity and Tritium?
Every country has its own regulations and laws regarding radioactive substances. It is crucial to comply with these and work with the relevant authorities. There are well-established markets like the USA, UK, and the Netherlands, as well as more restrictive ones like France. Generally, product registration, import and export licenses, as well as special transport and handling licenses, are required. Companies like mb-microtec are well-versed in these regulations and can provide the necessary services to acquire the required know-how and licenses.